Prostate cancer often doesn’t show symptoms in its early stages, making it a silent threat. Yet, in more advanced stages, symptoms like difficulty urinating, blood in urine, and bone pain can emerge. Recognizing these signs early is crucial to seeking timely medical attention. This cancer is a significant health concern worldwide, and knowing when to consult a doctor could be a step towards better outcomes.
Men may often overlook these symptoms or attribute them to less serious conditions. However, understanding when to consult a healthcare professional can make a difference. Any noticeable changes should prompt a conversation with a doctor. Prostate cancer impacts countless men, and being alert to symptoms can play a critical role in early detection and treatment.
By staying informed about prostate cancer statistics, individuals can better assess their risk and make informed decisions about their health. Being proactive in seeking a medical evaluation could be lifesaving.
Key Takeaways
- Recognize early symptoms like trouble urinating and blood in urine.
- Consult a doctor if symptoms seem unusual or persistent.
- Awareness of prostate cancer statistics helps understand personal risk.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Prostate cancer often shows symptoms that can signal the need for medical attention. These signs may relate to urinary changes or present as other indicators involving pain or discomfort. Understanding these symptoms can aid in seeking early diagnosis and treatment.
Urinary Changes
Changes in urinary habits are a common early sign of prostate cancer. Men might experience frequent urination, especially at night (nocturia), or have trouble starting and stopping while urinating. A weak urine flow or an urgent need to urinate can also occur. These symptoms can often be mistaken for other prostate health issues, but recognizing them is important for those who might be at risk. Consulting a healthcare provider can determine whether these changes are related to prostate cancer or another condition.
Potential Signs and Complications
Some symptoms go beyond the urinary system and can be more concerning. Blood in the urine or in the semen can be signs of prostate cancer. Painful ejaculation and erectile dysfunction might also suggest prostate issues. These symptoms point towards complications that should be evaluated by a urologist. Pelvic or bone pain and unexplained weight loss can also indicate more severe conditions. Prompt attention to these symptoms ensures timely medical intervention if needed.
Advanced Stage Indicators
In advanced stages of prostate cancer, symptoms may become more pronounced and diverse. Bone pain, especially in the spine, hips, or ribs, might signal the spread of cancer. Persistent pelvic pain can also be an indicator, alongside overall fatigue.
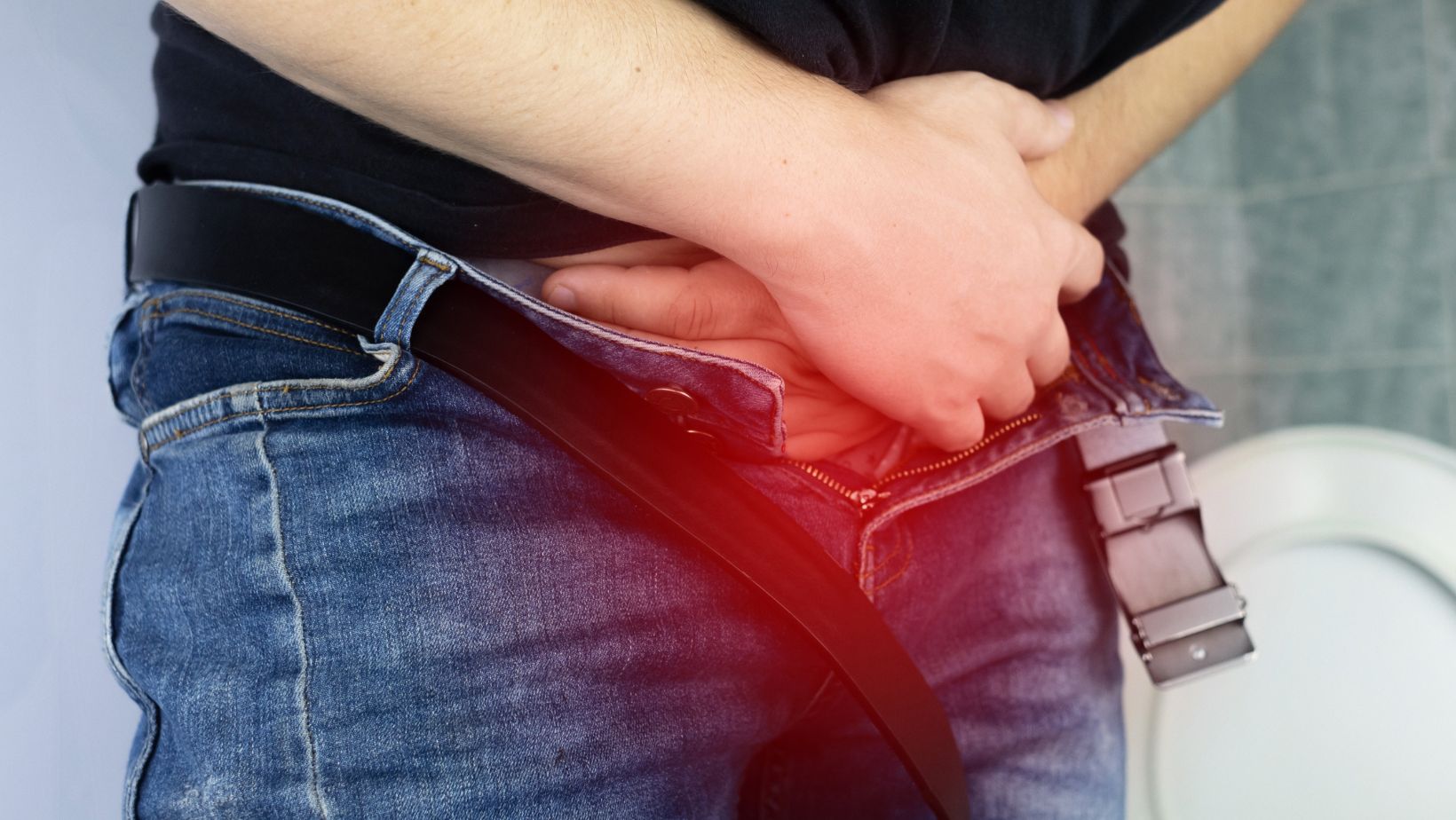

As cancer progresses, men might experience further weight loss or decreased appetite. Recognizing these more severe symptoms is crucial for engaging healthcare professionals early to manage the disease effectively.
When to Contact a Doctor
If you notice unusual symptoms or belong to a high-risk group, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. Early detection through screening and addressing risk factors can lead to more treatment options and improved outcomes.
Screening and Diagnosis
Regular screening for prostate cancer plays a key role in early detection. Men typically undergo a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, which measures PSA levels in the blood. Higher levels may suggest the presence of prostate cancer, prompting further investigation, such as a prostate biopsy.
The digital rectal exam (DRE) is another tool doctors use. During this exam, a urologist checks the prostate for abnormalities. These tests can guide the need for more comprehensive diagnostic methods and help manage the condition effectively.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing prostate cancer. These include age, as the risk rises significantly for men over 50, and family history, particularly if a close relative has had the disease.
Genetics also play a role, making it important for men with a family history of prostate cancer to discuss their risk with a doctor. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, such as following a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing weight, can help reduce the risk. Making informed lifestyle choices may lower the chances of developing prostate cancer, helping maintain better prostate health.
Conclusion
Prostate cancer can be a serious health issue for men. Early stages often show few symptoms, which makes it important for men to be aware of any subtle changes in their health. Common symptoms include frequent urination, weak urine flow, or discomfort in the pelvic area. These could be signs to seek medical advice.
Men should be especially attentive if they have risk factors such as age and family history. Regular check-ups and discussions with healthcare providers can help in early detection.
Seeking medical attention when symptoms are noticed improves the chances of effective treatment. Recognizing symptoms early helps individuals take timely action to manage their health.